The IT and communications industry is undeniably guilty of overusing acronyms. This can create confusion and misunderstanding, and LTE (Long-Term Evolution) is a classic example. Organizations sometimes mistakenly equate LTE with broadband internet – which is a problem, because clarity and precision are important in selecting the right kind of LTE connectivity for different Internet of Things (IoT) applications, as we’ll explore here.
The Different “Flavors” of LTE
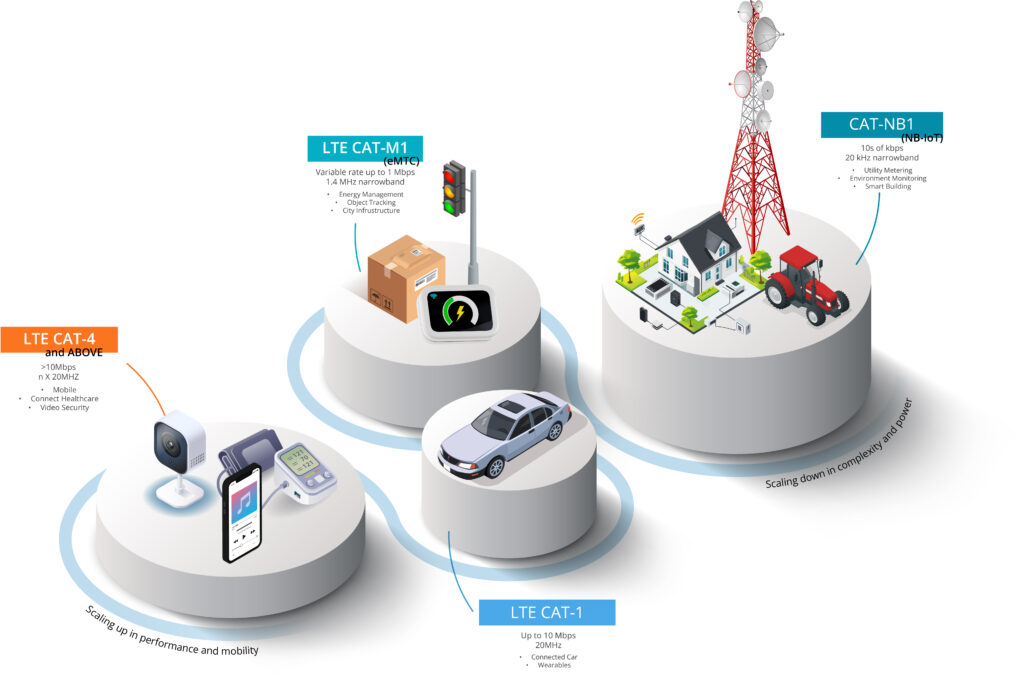
LTE isn’t a single solution. Instead, it covers several categories, each suitable for different use cases.
LTE-Advanced (CAT 6 and Beyond): Fast Speeds up to 300Mbps
LTE-Advanced (CAT 6 and Beyond) is widely available globally, having been deployed by more than 90% of mobile network operators in developed markets. In 2023, LTE-Advanced networks covered more than 75% of the global population, and user adoption rates are steadily increasing as consumers continue to demand faster and more reliable mobile internet connections.
LTE Advanced is ideal for high-speed, bandwidth-intensive applications such as video streaming, and it’s a popular choice for mobile devices that need robust internet connectivity with high speeds and low latency. It supports downlink speeds of up to 300Mbps, making it a significant step up in mobile connectivity compared to 3G.
LTE CAT 1: A Balance of Performance and Cost-Effectiveness
LTE Cat 1 is a widely adopted technology offering moderate speeds for applications such as low-bit-rate video streaming and voice support. It’s suitable for M2M (machine-to-machine) and IoT applications.
Despite being an older technology (having been introduced with 3GPP Release 8), LTE Cat 1 continues to hold its ground against newer alternatives like LTE-M and NB-IoT, particularly for use cases that only require moderate data rates and latency.
While LTE Cat 1 is more power-hungry and has a shorter signal range than low-power wide area network (LPWAN) technologies, it offers a higher data rate and lower latency.
The hardware costs for LTE Cat 1 can be higher than those for LPWAN devices, but the higher speeds, better coverage, and lower latency often justify the investment. This is particularly true where reliable, real-time data transmission is essential, such as with some IoT deployments.
LTE Cat 1 provides a robust migration path for 2G and 3G applications, enabling a smooth transition to more advanced networks without the need for significant redesign.
LTE Technologies Compared
| FEATURES | NB-IoT | LTE CAT 1 | LTE-M |
| Network Reach | Available in 60 countries with support from over 100 service providers | Connects to more than 800 4G LTE networks worldwide | Extends across more than 120 global networks |
| Data Throughput | Best suited to low-speed data transfers | Provides moderate data speeds with minimal delays | Offers high-speed data transfer for both sending and receiving |
| Adoption Rate | Growing presence requires new infrastructure in many areas | Widely adopted with extensive availability | Broadly available in areas with LTE coverage |
| Roaming | Roaming is technically feasible but not widely adopted | Reliable roaming capabilities | Strong roaming capabilities |
| Energy Consumption | Low power consumption with efficient power-saving features | Higher power usage | Includes power-saving features |
| Mobility Support | No handover capability, best for stationary applications | Supports handover, suitable for mobile use | Supports handover, ideal for mobile applications |
| Cost Consideration | More affordable module options | Relatively high costs, though prices are gradually decreasing | Module prices are generally high |
LTE Cat M (LTE-M): Power Saving for Longer Battery Life
LTE Cat M (LTE-M) is a low-power wide-area network (LPWAN) solution specifically designed to extend the battery life of IoT devices by optimizing power consumption.
Its development by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project focused on simplifying the device architecture with power efficiency in mind. By reducing peak speed capabilities and eliminating features such as carrier aggregation, higher-order modulation, and multiple antennas, LTE-M devices operate with narrower bandwidths – as low as 1.4 MHz. This streamlined architecture reduces the power needed for memory and processing, leading to a longer battery life.
LTE-M’s power-saving capabilities include:
- Simplified Architecture: LTE-M devices operate with only one antenna and support half-duplex communication, reducing the complexity and power requirements.
- Optimized Signalling: IoT devices using LTE-M do not need constant connectivity or seamless mobility, eliminating the need for frequent signalling and network measurements.
- Power Save Mode (PSM): PSM allows devices to wake up at scheduled intervals, transmit data, and then return to a low-power sleep mode. For example, a water meter might wake up once daily to send a reading and then go back to sleep, significantly reducing power consumption. An LTE-M device in full PSM mode that only transmits daily could last over ten years on just two AA batteries.
These power-saving enhancements make LTE-M an ideal choice for IoT applications that require devices to operate for extended periods without frequent battery replacement, such as smart meters, asset trackers, and environmental sensors.
NarrowBand-IoT (NB-IoT): Low Power and Wide Coverage
NarrowBand-IoT (NB-IoT) is tailored for low-power, wide-area applications, offering extended battery life, support for a higher density of devices, and superior indoor coverage.
Operating on a narrower bandwidth, NB-IoT optimizes spectrum usage and energy efficiency at the cost of lower data rates and excels in dense urban environments. This makes it ideal for massive device connectivity with minimal data transmission, such as in smart city infrastructure, smart agriculture, environmental monitoring, and industrial IoT systems.
Why Choose LTE for Your IoT Deployment?
Whether you’re a first-time IoT developer or planning a 2G/3G migration, there’s a connectivity solution to help you maximize the return on your investment – and with the widespread coverage of LTE and the ever-growing availability of LTE-M and NB-IoT, the options are increasing. Careful planning and collaboration with your connectivity solution provider will help you to identify the most viable options for your specific deployment needs and locations.
No matter which connectivity category you choose, LTE provides significant benefits for IoT projects:
- It’s highly scalable and accommodates multiple devices, making it an ideal choice for expansive IoT implementations.
- LTE networks offer advanced security measures like encryption and network authentication, so sensitive IoT data remains protected.
- The broad reach of LTE networks allows IoT devices to function effectively even in rural and remote areas.
- Its ability to deliver high-speed data is ideal for applications that demand real-time information transfer, such as video monitoring systems.
- The low latency provided by LTE is crucial where rapid response times are essential, such as in industrial automation and autonomous vehicles.
A Solution for Almost Every IoT Challenge
Understanding the options and selecting the best LTE variant for your individual needs is crucial to realize strong return on your investment.
The ongoing evolution of LTE technologies means there’s a suitable solution for a wide range of applications and use cases.
Whether it’s the scalability and security of traditional LTE, the cost-effectiveness of LTE Cat 1, the power efficiency of LTE-M, or the extensive coverage of NB-IoT, there is now a range of options designed to meet the needs of virtually every IoT deployment.
